Whether you’ve smoked it or been around friends who have, you know cannabis is something that gets you high. Even medical marijuana can get you high, right? And you might know that it’s due to tetrahydrocannabinol, better known as THC. That’s the compound found on cannabis plants with psychoactive effects, but it’s not the most frequent compound found in it.
Come the end of this year, it may not even be the most well-known compound. That is how quickly cannabidiol, aka CBD, is rising through the ranks and establishing itself as a common cultural term.
CBD has had a renaissance in the past few years. As more states make the push to , dispensaries continue to pop up containing a dizzying (not literally, though) array of CBD products for people to take in various forms. It’s proven to be a versatile compound.
It hasn’t been able to prove much else, though. That’s because notoriously anti-weed Attorney General Jeff Sessions, in addition to insisting authorities pursue marijuana cases, classified cannabis as a schedule 1 drug, a classification the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) uses for drugs they say have “no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse.” There’s minimal actual proof of the abuse potential, but this classification has made it much harder to research the benefits of CBD.
Still, with some studies out there suggesting medical benefits, and others trying to get off the ground, CBD is here to stay for now. So… what is it?
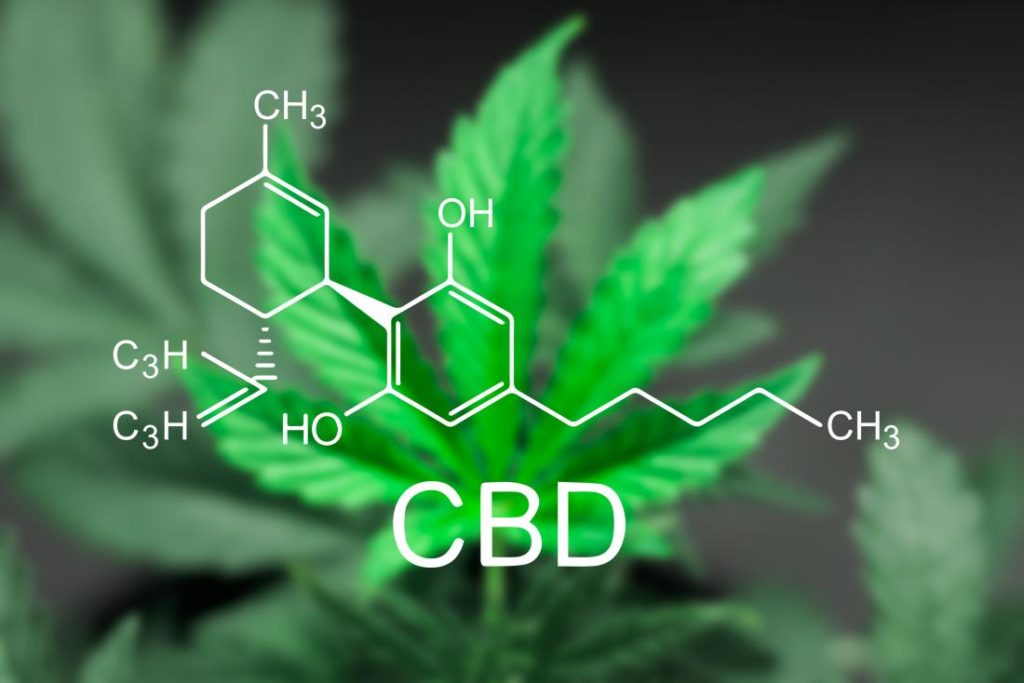
What is CBD?
CBD is a cannabinoid, one of hundreds of chemical compounds found on both marijuana plants and hemp plants, which has shown potential for having benefits ranging from pain relief to epilepsy treatment. Unlike THC, which is known for its psychoactive nature, CBD doesn’t get you high.
What it does have in common with THC, though, is that because they are both cannabinoids they impact our bodies and minds using cannabinoid receptors. These are a part of the endocannabinoid system inside the human body, which affects a number of different physiological processes. These receptors, to date found primarily in the nervous and immune systems, are what the CBD interacts with to give you the effects.
Not only does CBD not give users the high THC does, some studies suggest it may work to counteract some of the more negative THC effects, like paranoia and heightened anxiety. For this reason, often people that are looking for legal weed with THC will look for a strain with a solid THC to CBD ratio, chasing an ideal, centered high.
CBD Effects
Cannabidiol, in addition to not having the high effect of THC, can also counter the psychoactive effects of THC in more balanced strains. When used on its own or in a more CBD-heavy strain, it has shown helpful properties for the body and mind by assisting, among other things, pain management and insomnia treatment.
Need examples of the body and mind effects? Studies have shown that cannabidiol can actually have anti-inflammatory effects, which can have impacts on several different conditions. Other studies have focused on CBD having antipsychotic effects on the brain. CBD is said to have neuroprotective properties as well, beneficial to the nervous system and the brain.
Encouragingly, the World Health Organization (WHO) published a report in November 2017 that said that despite the classification as a Schedule 1 drug, so far “there is no evidence of recreational use of CBD or any public health related problems associated with the use of pure CBD.” The report suggested certain side effects like vomiting and fatigue, but determined it was likely due to other drugs it interacted with during medical studies.
Ultimately, the report suggested that although there are not a large number of studies that could provide more definitive results, what tests have been done found a lot of medical benefits with little harm.
CBD Benefits: How Can It Help Medically?
CBD has been linked to treatment in degenerative muscle conditions, depression, injury rehabilitation, chronic pain disorders, acne, high blood pressure and a bevy of other diseases and disorders. The scope of treatments CBD has been linked to in a limited number of studies is impressive.
Remember the anti-inflammatory properties CBD has? That may be able to help people suffering from rheumatoid arthritis. Studies that have posited this have similarly suggested that the anti-inflammatory nature can help in the treatment of multiple sclerosis, as well as inflammation that flares up as a result of hepatitis and bowel disorders like Crohn’s disease and colitis.
WHO’s report also suggests that CBD’s neuroprotective effects could potentially provide therapeutic treatment not just to multiple sclerosis, but perhaps Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease as well. It’s certainly possible and what little studies have been done on it suggests beneficial components, but unfortunately there has not been much official research done.
As some foundations and universities attempt to put more effort and money into what studies can be done considering federal laws, other disorders are getting studied as well – a number of clinical trials were recently announced to try to determine whether CBD is safe and effective for treating symptoms for children with severe autism.
The most prominent diseases and disorders CBD has been said to help, though, are epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and cancer.
CBD and Epilepsy
Cannabidiol’s medical benefits for epilepsy are likely the most notably studied ones – probably cause it has shown itself to be so effective for rare and severe epileptic disorders.
In 2017, the New England Journal of Medicine published the findings of a study focusing on CBD’s effects on Dravet syndrome, a rare and particularly dangerous epilepsy disorder found in children. Scientists found CBD to be exceptionally effective at lowering the frequency of seizures in patients – remarkable considering the genetic mutation of Dravet syndrome makes the seizures difficult to treat with medication.
Recently, the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) made waves by approving Epidiolex, a CBD medication meant to treat rare and severe forms of epilepsy.
CBD and Anxiety
Not content to be physically therapeutic, CBD has shown itself to have many mentally therapeutic benefits, none more so than it’s relief for those suffering from anxiety. Anti-anxiety drugs are known as anxiolytics, and studies done regarding CBD and a number of anxiety-related disorder have found that it has some anxiolytic capabilities as well.
The anti-anxiety benefits aren’t just relegated to general anxiety disorders – though if you’re searching for studies relating to them. Other studies have examined its effects on those suffering from depression. Others focused on anxiety relief for children suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). One study, published in 2015, found positive effects not only for the aforementioned disorder, but panic disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder as well.
CBD and Cancer
There have been many studies suggesting that marijuana and cannabidiol can be helpful in relieving problems arising from cancer treatment, such as nausea, vomiting, and pain caused by chemotherapy. But the potential CBD has for cancer treatment may be far greater than that. Some studies examined CBD use in breast cancer patients and found that it was actually inhibiting breast cancer cells from proliferating.
Should CBD ever get taken off the list of Schedule 1 drugs, further examining its role in helping cancer treatment may be what scientists will be most interested in studying.
What is CBD Oil?
CBD oil is the combination of cannabidiol, extracted from the marijuana plant, with an oil to carry it in, such as coconut or olive oil. This is easily the most popular form of ingesting CBD amongst both medicinal and recreational users in part because there are so many different ways of taking CBD oil, most notably vaping.
Because CBD oil can be vaporized, often cultivators will look to ensure it has a strong aroma and flavor to it. This is thanks to another compound found in marijuana (among other plants) known as terpenes. Terpenes give off very distinct flavors; depending on the specific terpene, marijuana users could get a strain that’s particularly fruity, earthy, floral or minty. It is thought that terpenes have their own medicinal and anti-inflammatory effects, and that they work in tandem with CBD to bring out the best in one another, a phenomenon known as the “entourage effect.” The aroma also plays a strong role in the marketing of CBD oils. Why buy generic oil when you can by lavender CBD oil?
Vaping is arguably the most common way of ingesting CBD oil but it’s far from the only way to do it. Another popular method is tinctures, a similar liquid form of CBD made by steeping the plant in grain alcohol and then boiling the spirit out of it. Tinctures are taken with a dropper, wherein you place droplets under your tongue – often in relatively small doses, as once the spirit is boiled out of the liquid you are left with CBD concentrate.
How Else Can CBD Be Taken?
CBD offers quite a few benefits, so it’s only fitting that there are as many, if not more ways to get it into your system. Not everyone likes smoking or vaping CBD, as smoking anything remains problematic for your lungs and vape pens are still new, so it can be difficult to ascertain just how safe they are. So where are you left in cases like that?
Here are just a few additional ways you can take CBD.
Concentrates. If you’re not put off by vaping, the term “concentrate” can mean a lot of things for CBD. It can sometimes refer to oil, but is essentially anything that is high-potency with regards to cannabidiol. Concentrates can also come in forms like wax or shatter, made somewhat similarly to how hard candy is made.
Food. Chocolates, cookies, gummies, brownies – marijuana enthusiasts are always looking for a new edible to try, and CBD product creators are always looking for a new one to create.
Drinks. A few coffee shops in states where cannabis is legal or decriminalized have been known to offer CBD coffee and tea. Some breweries on the west coast have CBD beer available, with cocktails available in select bars.
Dog treats. Well, you shouldn’t be eating them. But some dispensaries sell dog treats made from CBD-rich hemp meant to help pets with anxiety and/or pain.
Skin care products. These can be surprisingly practical. Skin care products that have CBD can be used for pain relief, acne treatment, wrinkles, or just relaxing therapeutic purposes.
Beauty products. Similarly, there is CBD shampoo, makeup, deodorant, and bath bombs designed to keep you clean and keep you relaxed.
Legality of CBD
The legality of CBD, like cannabis in general, is complicated and depends on a number of factors. For CBD, whether it is legal depends on the state you live in, its own marijuana laws, and whether the CBD is made of cannabis or hemp. If the CBD was extracted from legally cultivated hemp, for example, it should be legal as hemp has less than 0.3% THC.
If the CBD was extracted from cannabis, your local laws will determine the legality. The only states where CBD is entirely illegal Idaho, South Dakota, Kansas, and Nebraska. If you live in another state, check whether marijuana is legal at the recreational level or only at the medicinal level – if only medical marijuana has been legalized, you’ll need a prescription.
Of the states that have legalized marijuana on some level, only 9 states (and Washington D.C.) have fully legalized recreational use. 29 states, including those 9, have legalized marijuana for medical purposes. Of the states that still haven’t legalized medical marijuana, many still have exceptions for CBD to be prescribed for certain conditions. For most of these states, the exception that allows for medical CBD is epilepsy, but Georgia and Iowa allow it to be prescribed for several additional medical conditions.
Is CBD a Schedule 1 Drug?
Despite all the studies suggesting major medical potential when it comes to CBD, the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) continues to classify it, along with the rest of the cannabis plant, as a Schedule 1 drug. The DEA describes Schedule 1 drugs as “drugs with no currently accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse.”
It is part of the continuing contradictions with medical marijuana and the law; enough studies have shown positive effects that over half the states in the country have legalized it on some level, yet federally it is still seen as not having any medical use.
Its future as a Schedule 1 drug remains a question. The current administration seems set on keeping it that way, but does the FDA’s aforementioned approval of Epidiolex, the epilepsy drug with CBD, lead the DEA to potentially reclassifying CBD?